Repeated contractions of facial muscles create mechanical tension of the skin, provoking the formation of dynamic wrinkles. With age, a decrease in collagen and elastin production weakens the skin’s ability to repair, transforming dynamic wrinkles into static lines. In addition, this process is accelerated by environmental factors, such as ultraviolet radiation, which contributes to the degradation of structural proteins. To slow down these changes, botulinum toxin is used to reduce muscle activity, while the synthesis of structural proteins is stimulated to preserve skin elasticity.
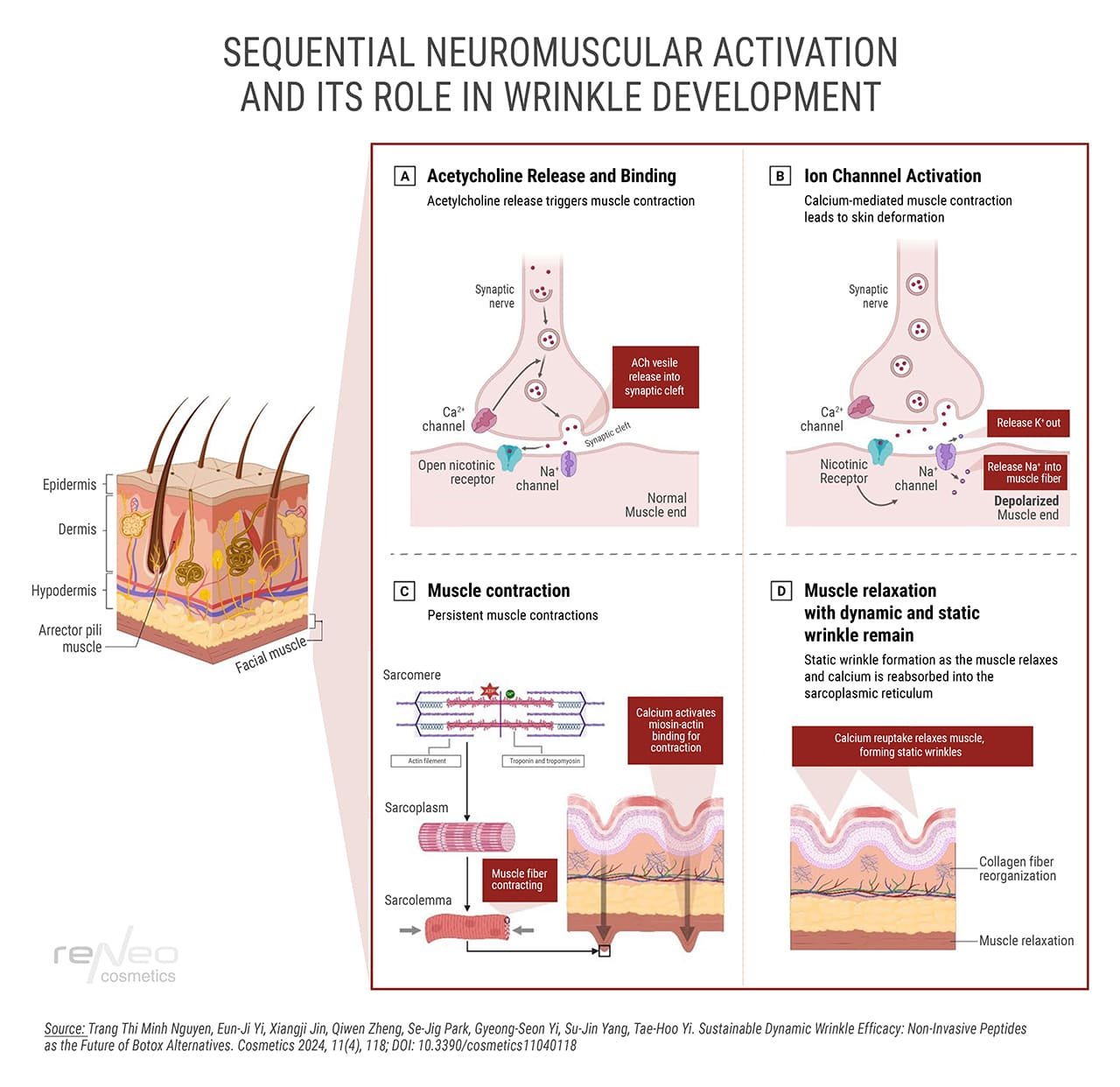
However, despite the proven effectiveness of botulinum toxin type A, the invasiveness of this procedure and the strict limitations in its use contribute to the active growth of interest in non-injection alternatives.
Botulinum-like peptides are synthetic equivalents of the active components of botulinum toxin, designed to affect neuromuscular transmission without the need for injections. They are similar to botulinum toxin, but have a number of features that make them safer and more convenient for use in cosmetic products for external use.
Structure of botulinum-like peptides
Botulinum-like peptides may have structural homology with certain domains of botulinum toxin, which ensures their ability to interact with key proteins in nerve cells. Botulinum toxin consists of three main functional domains:
- Translocation domain (T-domain) — ensures the transport of the toxin across the cell membrane.
- Binding domain (H-domain) — is responsible for binding to receptors on the surface of neurons.
- Catalytic domain (L-domain) — has protease activity and breaks down proteins involved in the fusion of synaptic vesicles (such as the SNARE complex).
Botulinum-like peptides usually contain regions similar to the L-domain and can selectively affect components of the SNARE complex (Synaptobrevin, SNAP-25 and Syntaxin), which causes inhibition of neurotransmitter exocytosis.
SNARE (Soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor Attachment protein Receptor) — a large group of proteins that carry out the fusion of intracellular transport vesicles with the cell membrane (exocytosis) or with a target organelle, such as a lysosome.
SNAP-25 (Synaptosomal Associated Protein) — membrane protein, a component of the SNARE protein complex, which ensures the fusion of the synaptic vesicle with the presynaptic membrane of the neuron and their association with the subsequent release of the neurotransmitter.
Mechanism of action of botulinum-like peptides
Botulinum toxin blocks motor and parasympathetic nerve function by reducing the release of acetylcholine, avoiding neutralization by antibodies, although the onset of muscle paralysis is delayed. This process involves binding of the toxin to nerve terminals, internalization and subsequent destruction of SNAP-25, a protein required for synaptic vesicle fusion, and interaction with other proteins such as syntaxin (a t-SNARE involved in vesicle fusion) and VAMP/synaptobrevin (a v-SNARE critical for vesicle fusion).
Botulinum-like peptides can act similarly to botulinum toxin (inhibiting the release of acetylcholine) or through muscle cell receptors.
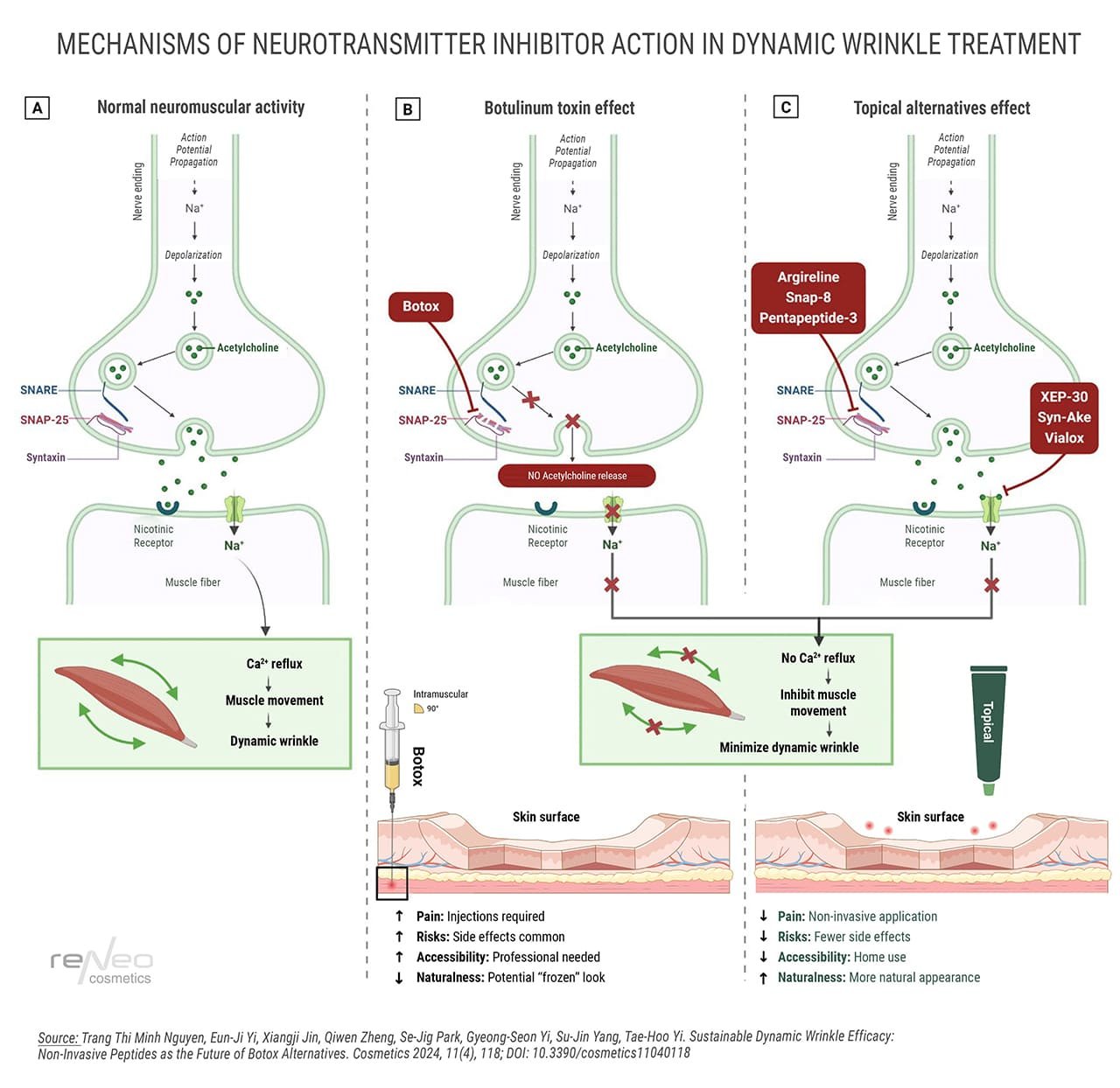
The main mechanism of action of botulinum-like peptides is the inhibition of components of the SNARE complex, which are key to the process of vesicle fusion with the membrane and the release of acetylcholine into the synaptic cleft. Under normal conditions, SNARE proteins, such as Synaptobrevin (VAMP), Syntaxin and SNAP-25, form a complex necessary for vesicle exocytosis.
Botulinum-like peptides bind to proteins of this complex, blocking their conformational interaction and preventing the formation of a stable SNARE structure. This reduces the release of acetylcholine, which weakens the contraction of facial muscles and contributes to the smoothing of superficial wrinkles.
An additional mechanism of action is associated with the inhibition of calcium-dependent pathways that regulate the exocytosis of neurotransmitters. Peptides can reduce the sensitivity of nerve endings to calcium ions, preventing the activation of calcium-dependent proteins involved in the synthesis and release of acetylcholine. This reduces the excitability of neurons, which further weakens the activity of facial muscles. Some botulinum-like peptides are also able to interact with receptors on the surface of skin cells and modulate their activity. This includes inhibiting the activity of receptors that mediate signal transmission from nerve endings to muscle fibers. In addition, peptides can reduce the activity of tyrosine kinase cascades, which leads to a decrease in the synthesis of inflammatory mediators and a decrease in oxidative stress in dermal cells.
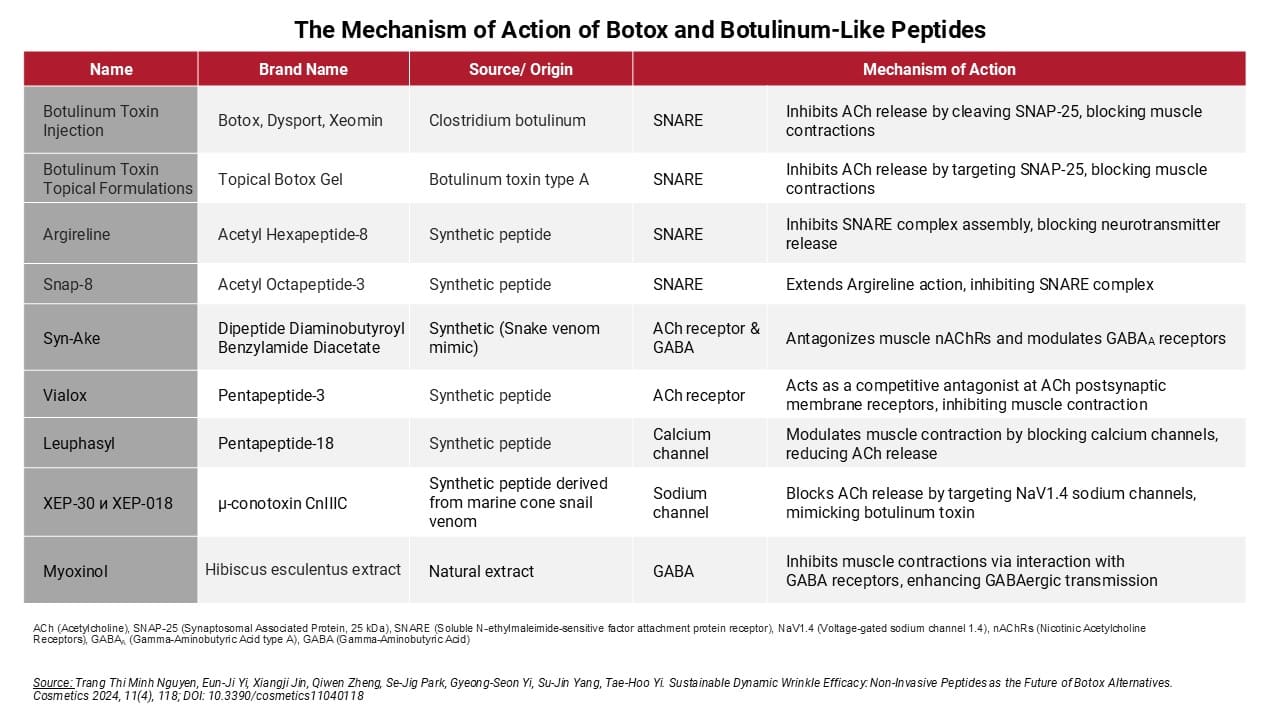
The most effective botulinum-like peptides in cosmetology today
Today, there is a wide range of botulinum-like peptides of both synthetic and natural origin. The most effective of them are Argireline (Acetyl Hexapeptide-8) and Syn-Ake (Dipeptide Diaminobutyroyl Benzylamide Diacetate), which are able to reduce wrinkles by up to 52% within four weeks without injections.
Acetyl-hexapeptide-8 (Argirelin)
Argirelin is a short peptide that structurally resembles the N-terminal fragment of the SNAP-25 protein, which is part of the SNARE complex (Synaptobrevin, SNAP-25, Syntaxin).
- Mechanism of action:
Argirelin competitively binds to the active sites of the SNAP-25 protein, disrupting its conformational interaction with Synaptobrevin and Syntaxin. Since the SNARE complex is necessary for the fusion of synaptic vesicles with the membrane, this mechanism reduces the release of acetylcholine into the synaptic cleft. As a result, the transmission of nerve signals is temporarily reduced, muscle contractions are weakened, which contributes to the smoothing of wrinkles. - Benefits:
Acetyl hexapeptide-8 is one of the most studied and popular botulinum peptides in cosmetology. It has a high ability to penetrate the epidermal barrier and is safe for long-term use due to the reversible effect. - Clinical studies:
- A study by Blanes-Mir et al. (2002) demonstrated a 30% reduction in wrinkle depth after 30 days of using a 10% argireline solution.
- Another study (2013) showed a 48.9% efficacy of argireline in reducing wrinkles after four weeks of use.
It is due to argireline that a pronounced smoothing effect is achieved when using Anti-Wrinkle Mask from reNeo cosmetics, an Alginate mask with muscle relaxing effect. Furthermore, the inclusion of Dictyopteris brown algae in the mask enhances its efficacy by delivering a plumping and filler-like effect, and the Homeostatine™ complex restores homeostasis of the extracellular matrix and suppresses the activity of metalloproteinases and the synthesis of pro-inflammatory cytokines. The mask reduces the depth and number of wrinkles, makes the skin elastic and firm.
The rich composition of Vita-Active Peptide Serum, which includes Acetyl-hexapeptide-8, vitamins A, B, C, E, 5 growth factors, folic acid, provides a comprehensive anti-age effect. In addition to smoothing fine wrinkles, this multifunctional serum restores the skin’s lipid barrier, prevents dehydration, brightens the skin and evens out its tone.
Syn-Ake (Tripeptide-3, Dipeptide Diaminobutyroyl Benzylamide Diacetate)
Syn-Ake is a synthetic tripeptide equivalent that mimics the active components of snake neurotoxins, such as waglerin-1, derived from the venom of the temple hooded snake (Tropidolaemus wagleri).
- Mechanism of action:
Syn-Ake works as a competitive antagonist of nAChR receptors on the postsynaptic membrane, blocking their activation by acetylcholine. This prevents depolarization of muscle cell membranes and muscle contraction. Blocked receptors do not allow sodium and potassium ions to pass through, resulting in the transmission of nerve signals, muscle fibers relaxing and wrinkles being reduced. - Benefits:
Syn-Ake provides localized muscle relaxation. Targeted neuromodulation reduces the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles without affecting other cellular processes. This results in a high safety profile for topical use. Syn-Ake is therefore suitable for the correction of expression lines in the forehead and around the eyes. - Clinical studies:
According to the results of clinical studies, the use of a topical product with Syn-Ake for 28 days resulted in a 52% reduction in wrinkle size. Study participants reported a significant improvement in skin texture and a reduction in wrinkle depth. The effect was noticeable after just one week of use.
In the Anti-Wrinkle Serum from reNeo cosmetics, the muscle relaxant Syn-Ake demonstrates both immediate and prolonged action. Relaxation of facial muscles helps smooth wrinkles, and an additional effect is achieved thanks to the hyaluronic acid in the composition.
Synergy of the two peptides
Since Argireline and Syn-Ake have different mechanisms of influence on the release of acetylcholine, their use within the same care protocol allows you to synergistically enhance the effect of the procedure. This combination is provided in the Moisturizing Care with Muscle Relaxing Effect from reNeo cosmetics, which provides a comprehensive approach to combating wrinkles.
“Moisturizing Care with Muscle Relaxing Effect”
• Procedure Protocol >>
• Training Video >>
Key features of the use of botulinum-like peptides
Non-invasiveness. Unlike injection methods, botulinum-like peptides are applied topically as part of creams, serums, masks and other cosmetics. This eliminates the risk of tissue damage and complications such as swelling, hematomas or infections.
Reversibility and mildness of action. The effect of botulinum-like peptides is less pronounced compared to botulinum toxin, but reversible, which eliminates the risk of prolonged muscle paralysis. After discontinuation of use, normal facial activity is restored.
Delayed, cumulative effect. Peptides act gradually. Regular use of products with botulinum-like peptides contributes to the accumulation of the effect and a stable improvement in skin condition.
Safety for long-term use. Unlike botulinum toxin, which with frequent use can cause the production of antibodies and a decrease in effectiveness, botulinum peptides do not cause an immune response and can be used for a long time without losing the effect.
Botulinum-like peptides are suitable for a wide range of users and can be used in different age groups.
Prevention of the first signs of aging (25-35 years):
- Ideal for preventing the formation of facial wrinkles and maintaining skin elasticity.
- Recommended for the prevention of fine lines around the eyes, on the forehead and at the corners of the mouth.
Correction of age-related changes (35-50 years):
- Effective for the first signs of aging, such as shallow wrinkles and loss of elasticity.
- Recommended for those who want to avoid invasive procedures such as Botox injections.
Support for mature skin (50+ years):
- Used as part of a comprehensive anti-aging care to reduce deep wrinkles.
- In combination with other active ingredients (hyaluronic acid, retinoids), they enhance skin regeneration and improve its texture.
Skin maintenance between Botox injections:
- Prolong the effect of Botox injections through supportive home care.
- Improve skin quality through complex cosmetic formulations with botulinum peptides.
Thus, products based on botulinum peptides are an effective and safe alternative to Botox injections for those looking for a gentle and reversible way to combat facial wrinkles. They are suitable for both prevention and correction of age-related changes, and can be used as part of a comprehensive anti-aging care without the risk of serious side effects.
In addition, the use of products with botulinum peptides helps to prolong the effect of Botox and improve skin quality in the period between injections. In this case, it is important to give preference to complex formulations or additionally include products that stimulate the synthesis of dermal matrix components, such as collagen and elastin, in home care.
- Trang Thi Minh Nguyen, Eun-Ji Yi, Xiangji Jin, Qiwen Zheng, Se-Jig Park, Gyeong-Seon Yi, Su-Jin Yang, Tae-Hoo Yi. Sustainable Dynamic Wrinkle Efficacy: Non-Invasive Peptides as the Future of Botox Alternatives. Cosmetics 2024, 11(4), 118; DOI: 10.3390/cosmetics11040118
- Blanes-Mira, C.; Clemente, J.; Jodas, G.; Gil, A.; Fernández-Ballester, G.; Ponsati, B.; Gutierrez, L.; Pérez-Payá, E.; Ferrer-Montiel, A. A Synthetic Hexapeptide (Argireline) with Antiwrinkle Activity. International Journal of Cosmetic Science. 2002, 24, 303–310. DOI: 10.1046/j.1467-2494.2002.00153.x
- Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Xiao, S.; Pan, P.; Li, P.; Huo, J. The Anti-Wrinkle Efficacy of Argireline, a Synthetic Hexapeptide, in Chinese Subjects: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study. American Journal of Clinical Dermatology. 2013, 14, 147–153.
- dsm.com. An Effective Synthetic Peptide Ingredient Found in the Venom of the Temple Viper 2024. Available online: https://www.dsm.com/personal-care/en_US/products/skin-bioactives/syn-ake.html# (accessed on 1 June 2024).
- Gok, B.; Budama-Kilinc, Y.; Kecel-Gunduz, S. Anti-Aging Activity of Syn-Ake Peptide by in Silico Approaches and in Vitro Tests. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics. 2024, 42, 5015–5029. DOI: 10.1080/07391102.2023.2223681



