WHAT DOES THE LIPID BARRIER OF THE SKIN CONSIST OF?
The hydrolipid barrier of the skin is a protective layer consisting of sebum, sweat, organic acids, remnants of corneocytes and microflora covering the epidermis. It plays a key role in maintaining the health and hydration of the skin, preventing moisture loss and protecting against harmful external factors.
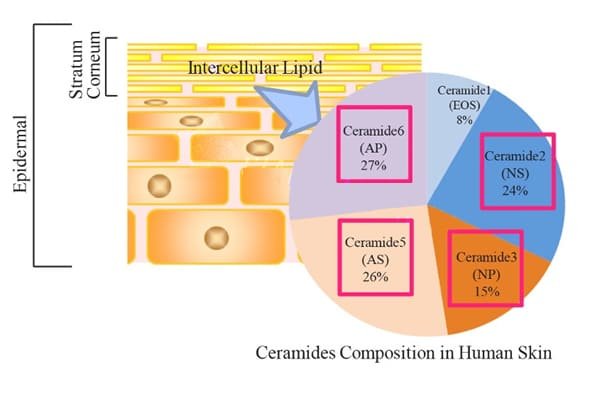
The hydrolipid barrier consists not only of oils on the skin surface, but also of highly specialized intercellular lipids. These include: ceramides, glycosylceramides, phospholipids, cholesterol, fatty acids, sphingoid bases, etc. All these substances have one common substrate in the form of fatty acids.
Fatty acids are important components that play a key role in biochemical processes in the skin. They are the main structural components of cell membranes, embedded in lipid bilayers that form membrane bilayers, ensuring the structural integrity of cells and regulating their permeability. Also, fatty acids provide energy, participate in the synthesis of lipids and other molecules.
The body can synthesize replacement (saturated) fatty acids independently from other molecules. They are not considered necessary in the diet. Essential (unsaturated) fatty acids are necessary, which cannot be synthesized in the body on their own, so they must come with food. Essential fatty acids such as omega-3 and omega-6 can influence skin inflammation and the immune response. They can have anti-inflammatory properties and participate in the regulation of the immune system. They have antioxidant properties, helping to protect skin cells from damage by free radicals.
Fatty acids are precursors for the synthesis of various lipids and other biochemically important molecules, such as hormones.
The overall composition and ratio of different fatty acids affect the health and condition of the skin. Consuming fatty acids through food or using cosmetic products with them can help maintain the health and appearance of the skin.
THE MAIN FUNCTIONS OF THE LIPID BARRIER
The lipid barrier performs several important functions:
- Protection from external factors – prevents the penetration of harmful substances and microorganisms into the internal environment
- Regulation of water balance – keeps moisture in the skin, preventing its evaporation. Preserving the skin’s structure, elasticity, and tone, the lipid barrier prevents premature aging.
When the skin barrier is disrupted or damaged, it cannot perform these tasks effectively.
WHAT FACTORS INFLUENCE THE VIOLATION OF THE SKIN BARRIER?
With age, the reserves of natural skin lipids are depleted. And people with chronically dry skin often lack a strong lipid barrier.
However, not only age changes and genetic predisposition contribute to the damage of the lipid barrier. Among the most common triggers, it is worth noting:
- Environmental impact. Various external factors, such as ultraviolet radiation, wind, low humidity and air pollution, can weaken the lipid barrier of the skin, making it vulnerable.
- Improper skin care. The use of aggressive cleansing ingredients or insufficient restoration of oils can break the lipid barrier. It is especially harmful to use products containing alcohol and aggressive chemical components, such as acids and retinol
- Stress and poor nutrition. Constant stress and lack of nutrients, such as vitamins and minerals, can negatively affect the condition of the skin. An insufficient amount of nutrients can reduce the ability of the skin to regenerate and protect.
CONSEQUENCES OF DISRUPTION OF THE SKIN LIPID BARRIER
Due to the weakening of the lipid barrier of the skin, harmful toxins and allergens can penetrate the skin, causing an inflammatory reaction of the immune system.
A violation of the skin barrier can clinically manifest in the following ways:
- Dryness and peeling, increased loss of moisture from tissues, which can lead to skin dehydration. At the cellular level: transepidermal moisture loss increases, saturation of the natural moisturizing factor decreases – lack of moisture-retaining components (amino acids, hyaluronic acid)
- Activation of inflammatory processes. A broken barrier allows conditionally pathogenic microorganisms to actively multiply, the local immunity of the skin decreases. The reactivity of Langerhans cells (cells of the immune system) increases, the synthesis of BAC (interleukins, prostaglandins) increases, which stimulates the division of keratinocytes and leads to manifestations of hyperkeratosis.
- Worsening of the skin’s general condition can lead to increased sensitivity, a dull complexion, and loss of elasticity. The likelihood of developing couperosis, wrinkles, and hyperpigmentation also increases. While lipid synthesis ramps up, this process takes time and resources.

HOW TO RESTORE THE LIPID BARRIER?
Restoration and maintenance of the lipid barrier requires a comprehensive approach:
Proper skin care
It is necessary to use mild cleansing ingredients and products containing nourishing, moisturizing components to restore the lipid barrier. It is important to avoid aggressive components and maintain a regular skin care regimen.
Regular cleansing of the skin
Regular, but not excessive, cleansing of the skin helps remove impurities and excess sebum without disrupting the lipid barrier. It is recommended to use mild cleansers without aggressive active ingredients that excessively reduce the oiliness.
Enzymes are ideal for such purposes. Plant enzymes delicately and gently destroy the connections between horny scales, eliminating excess sebum, leveling the skin surface.
Soft -Peeling Enzyme Mask contains papaya extract, which has excellent antioxidant, antiaging and strengthening properties. Papain is a proteolytic enzyme of the protease class that stimulates the breakdown of proteins into amino acids. It weakens the adhesion of corneocytes due to the destruction of structural bonds of desmosomes, which facilitates the exfoliation of horny scales, and also has an antimicrobial effect. Papain stimulates the cellular metabolism of the skin, which is necessary to maintain the osmotic balance in the epidermis. Vitamin B9, found in papaya, plays a role in cell renewal and helps maintain a healthy immune system for the skin. Exfoliating granules provide atraumatic exfoliation of corneocytes of the stratum corneum without damaging the lipid barrier of the skin.
Use of moisturizing and protective ingredients
Using nourishing ingredients such as fatty acids, ceramides, and natural oils helps restore and maintain the skin’s lipid barrier. Components rich in organic silicon support the skin’s moisture retention and elasticity. Soft-Balance Clay Mask provides powerful detoxification, evens out skin tone, moisturizes, and nourishes the skin while restoring its protective barrier. The mask contains kaolin, which absorbs excess sebum and cleanses the pores. A cocktail of light oils in the composition helps restore the skin’s corneobalance.
The balanced composition of meadowfoam oils, jojoba and glycosphingolipids in Lipid Balancing Light Cream fill the lack of fatty acids, form hydrophilic channels, contributing to the delivery of active components to the deeper layers of the skin. Glycosphingolipids enhance the synthesis of ceramides, while being a substrate for the restoration of cell membranes. The cream perfectly restores the lipid barrier, normalizes the qualitative and quantitative composition of fatty acids on the surface of the epidermis, increases the protective properties of the skin and prevents moisture loss.
It is also important to use sunscreen to protect against UV radiation at all times.
Following these recommendations will help maintain a healthy skin condition and protect the skin from damage, keeping it young and beautiful.